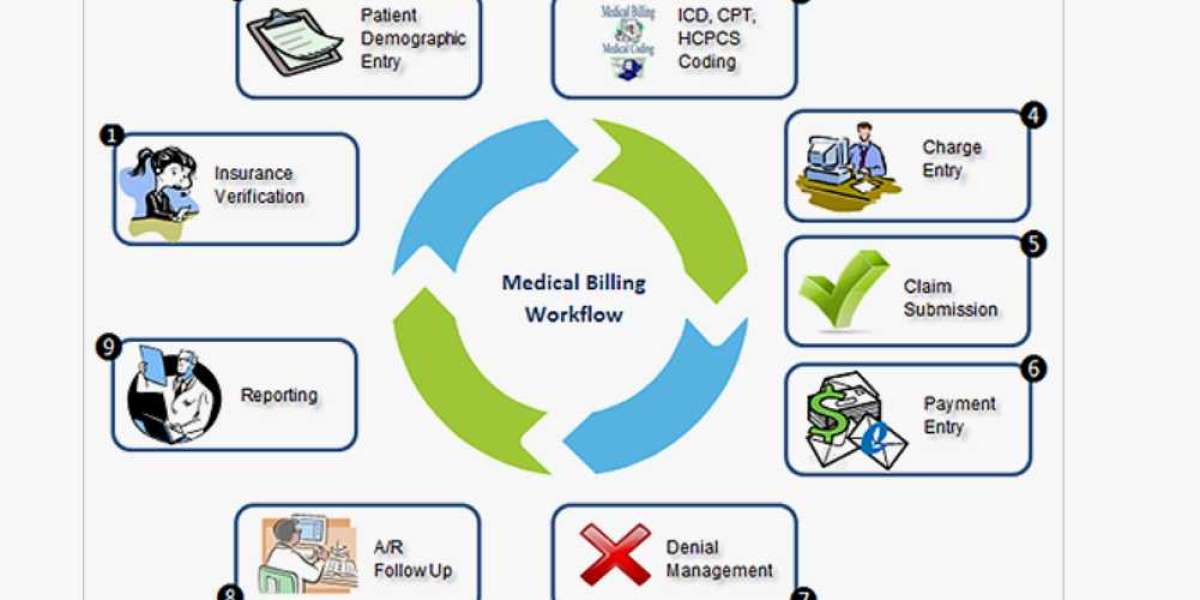
The basic medical billing workflow serves as the backbone of modern healthcare systems, bridging the gap between healthcare providers and insurance companies while ensuring patients receive accurate and timely billing services. This workflow, which may appear complex at first glance, is essential to maintaining a well-functioning healthcare ecosystem. It involves a series of meticulously planned steps, each designed to streamline the billing process and eliminate errors. To fully grasp the nuances of this topic, let’s dive into the core elements of the workflow, its critical stages, and the impact it has on healthcare services.
Step 1: Patient Registration and Demographic Collection
The medical billing process begins with patient registration, an essential step that ensures all necessary information is gathered at the outset. During registration, administrative staff collect vital details such as the patient’s name, address, date of birth, and contact information. Additionally, insurance details, including the policy number and provider, are documented to confirm eligibility. Accuracy at this stage is critical, as any errors can lead to claim denials or delays. For new patients, this step involves creating a unique medical record, while for returning patients, the data is updated as needed.
Step 2: Insurance Verification and Eligibility Check
Once the registration is complete, the next step is to verify the patient’s insurance details. This process involves confirming the validity of the insurance policy, understanding coverage limits, and determining out-of-pocket costs such as deductibles and copayments. Insurance verification is crucial to avoid potential claim rejections and to provide the patient with a clear understanding of their financial responsibilities. Healthcare providers often rely on electronic tools and real-time portals to expedite this process.
Step 3: Encounter and Charge Capture
During the patient’s visit, healthcare providers document the services rendered, including consultations, diagnostic tests, procedures, and any other medical interventions. Each service is assigned specific codes, known as Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, which serve as standardized identifiers for billing purposes. Simultaneously, the diagnosis is coded using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes. This stage, often referred to as charge capture, ensures that all services provided are accurately documented and ready for billing.
Step 4: Medical Coding
Medical coding is a specialized process where trained professionals translate the documented services and diagnoses into standardized codes. These codes play a critical role in billing and insurance claims, as they ensure consistency and compliance with regulations. Coders rely on tools such as the ICD and CPT codebooks to assign accurate codes, which form the basis of the medical bill. Proper coding reduces the risk of claim denials and facilitates smooth communication between healthcare providers and insurance companies.
Step 5: Claims Submission
Once coding is complete, the claim is prepared and submitted to the patient’s insurance provider. This step involves creating a clean claim, which means all necessary information is included, and no errors are present. Claims are typically submitted electronically through clearinghouses, which act as intermediaries between healthcare providers and insurance companies. The use of electronic claims submission ensures faster processing and reduces administrative burdens.
Step 6: Insurance Adjudication
After the claim is submitted, the insurance company reviews it to determine its validity, coverage, and payment amount. This process, known as adjudication, involves evaluating the claim against the patient’s insurance policy and identifying any discrepancies or missing information. The insurer may approve, deny, or request additional information to process the claim. Transparency and communication during this stage are vital to resolving any issues promptly.
Step 7: Payment Posting
Once the insurance company approves the claim, the payment is processed and posted to the patient’s account. Payment posting provides a detailed breakdown of the insurer’s payment, the patient’s financial responsibility, and any adjustments made. This step ensures that both the provider and patient have a clear understanding of the financial transaction and that any remaining balance is accounted for.
Step 8: Patient Billing and Collections
If there are outstanding balances after insurance payments, the healthcare provider generates a patient bill. This bill outlines the services provided, the insurance coverage applied, and the amount due from the patient. Clear and concise billing statements improve patient satisfaction and reduce confusion. In cases where payments are not made promptly, providers may initiate collections processes to recover the remaining amount.
Step 9: Follow-Up and Denial Management
Denial management is an integral part of the medical billing workflow. When claims are denied, the healthcare provider investigates the reasons, corrects any errors, and resubmits the claim. Effective follow-up ensures that payments are received promptly and that financial losses are minimized. Providers may use dedicated teams or automated tools to manage this aspect efficiently.
Step 10: Reporting and Analytics
The final stage in the medical billing workflow involves analyzing data and generating reports to evaluate the efficiency of the process. Metrics such as claim approval rates, denial rates, and payment turnaround times provide valuable insights into areas for improvement. By leveraging analytics, healthcare providers can optimize their billing practices and enhance overall financial performance.
Conclusion
The basic medical billing workflow is a comprehensive process designed to streamline healthcare payments and ensure accurate compensation for providers. By understanding the key steps, such as patient registration, coding, claims submission, and denial management, healthcare organizations can enhance their operational efficiency and improve patient satisfaction.
FAQ
- What is the purpose of medical billing?
Medical billing ensures that healthcare providers are compensated for their services by accurately processing claims and managing patient accounts. - How does insurance verification impact billing?
Insurance verification helps determine a patient’s coverage and avoids claim rejections by ensuring all details are accurate before the services are provided. - Why is medical coding essential?
Medical coding translates healthcare services into standardized codes, enabling accurate billing and compliance with insurance requirements. - What happens during claims adjudication?
Insurance companies review submitted claims to assess their validity and determine the payment amount based on the patient’s coverage. - How are denied claims managed?
Denied claims are reviewed to identify errors or missing information, corrected, and resubmitted for approval.
6. What role does reporting play in medical billing?
Reporting provides insights into billing efficiency, helping providers optimize their processes and improve financial outcomes.