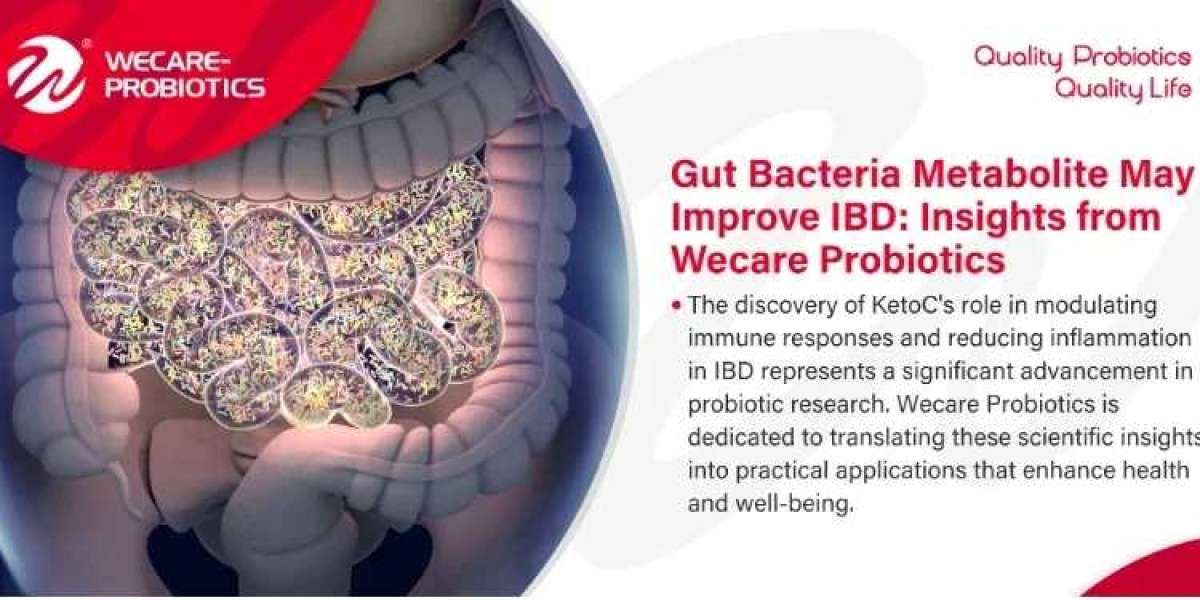
In a groundbreaking study published in Frontiers in Immunology, researchers from Tokyo University of Science have uncovered a potential mechanism by which gut bacteria can positively influence inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This discovery has significant implications for the probiotic industry, including companies like Wecare Probiotics Co., Ltd., which is dedicated to the research and development of probiotic strains and their applications.
Key Findings of the Study
The study, led by Professor Chiharu Nishiyama, explored the anti-inflammatory effects of a gut bacteria-generated linoleic acid metabolite known as KetoC. The research highlighted how gut microbiome metabolites, particularly those derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) like linoleic acid, can modulate immune responses and reduce inflammation in IBD.
In Vitro Insights:
The research focused on the effects of PUFA derivatives, specifically the metabolites of linoleic acid: KetoC, alpha-KetoC, and gamma-KetoC.
These enon derivatives markedly reduced levels of interleukin 2, a protein that triggers immune cell expansion and inflammation.
The original PUFAs did not show the same effects, underscoring the importance of bacterial conversion in activating their immunomodulatory properties.
Gamma-KetoC, in particular, was found to suppress prolonged T-cell proliferation and dendritic cell activation, both of which are linked to inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
The study also highlighted the involvement of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) and the transcription factor NFR2 in mediating these effects, with gamma-KetoC stimulating the NRF2 signaling pathway to suppress inflammatory cytokine production.
In Vivo Insights:
The in vitro findings were validated using a mouse model of IBD.
Gamma-KetoC treatment significantly reduced fibrosis-induced tissue damage in the colon, colitis-induced weight loss, and improved stool scores.
Treated mice showed decreased epithelial cell disruption, reduced infiltration of immune cells, and lower serum levels of inflammatory factors.
Mice deficient in NRF2 showed significant restoration following gamma-KetoC treatment, indicating the crucial role of this pathway in mediating the metabolite's anti-inflammatory effects.
Implications for Probiotic Development
The findings from this study align closely with the mission of Wecare Probiotics Co., Ltd., a pioneering national high-tech enterprise focused on advancing probiotic research and applications. Our company specializes in the development of probiotic strains, fermented food strains, and probiotic preparations tailored for various industries, including food, dairy, dietary supplements, precision medicine, personal care, feed additives, and pets.
At Wecare Probiotics, we continuously monitor the latest advancements in probiotic research to enhance our product offerings and application solutions. The discovery of KetoC's anti-inflammatory properties opens up new possibilities for developing targeted probiotic therapies for inflammatory diseases like IBD.
The Role of Wecare Probiotics
Wecare Probiotics is committed to leveraging cutting-edge research to improve human health through innovative probiotic solutions. Our expertise in probiotic strains and fermented food technologies positions us at the forefront of this rapidly evolving field. By understanding the mechanisms by which gut bacteria influence inflammation and immune responses, we can develop more effective probiotic products to support digestive health and overall well-being.
Our Focus Areas:
Intestinal Flora: Enhancing the balance of gut microbiota to promote digestive health and prevent dysbiosis-related disorders.
Human Health: Developing probiotic strains that support immune function, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health outcomes.
Fermented Food Strains: Innovating in the field of fermented foods to create products that deliver both nutritional and therapeutic benefits.
Future Directions
The study by Tokyo University of Science underscores the importance of detailed analyses at the individual, cellular, and genetic levels to understand how dietary components influence immune cell function. Wecare Probiotics aims to integrate these insights into our RD processes to develop next-generation probiotic products.
Potential future directions include:
Functional Foods and Supplements: Creating probiotic-enriched foods and dietary supplements that harness the anti-inflammatory properties of metabolites like KetoC.
Precision Medicine: Developing personalized probiotic therapies tailored to individual microbiome profiles to treat and prevent inflammatory diseases.
Expanded Applications: Exploring new applications for probiotic strains in areas such as personal care, pet health, and beyond.
Conclusion
The discovery of KetoC's role in modulating immune responses and reducing inflammation in IBD represents a significant advancement in probiotic research. Wecare Probiotics Co., Ltd. is dedicated to translating these scientific insights into practical applications that enhance health and well-being. As we continue to explore the frontiers of probiotic innovation, we remain committed to offering comprehensive solutions that meet the diverse needs of our customers across various industries.
For more information about our products and services, please visit product.
By staying at the cutting edge of probiotic research and development, Wecare Probiotics is poised to lead the industry in creating effective, science-backed probiotic solutions for a healthier future.