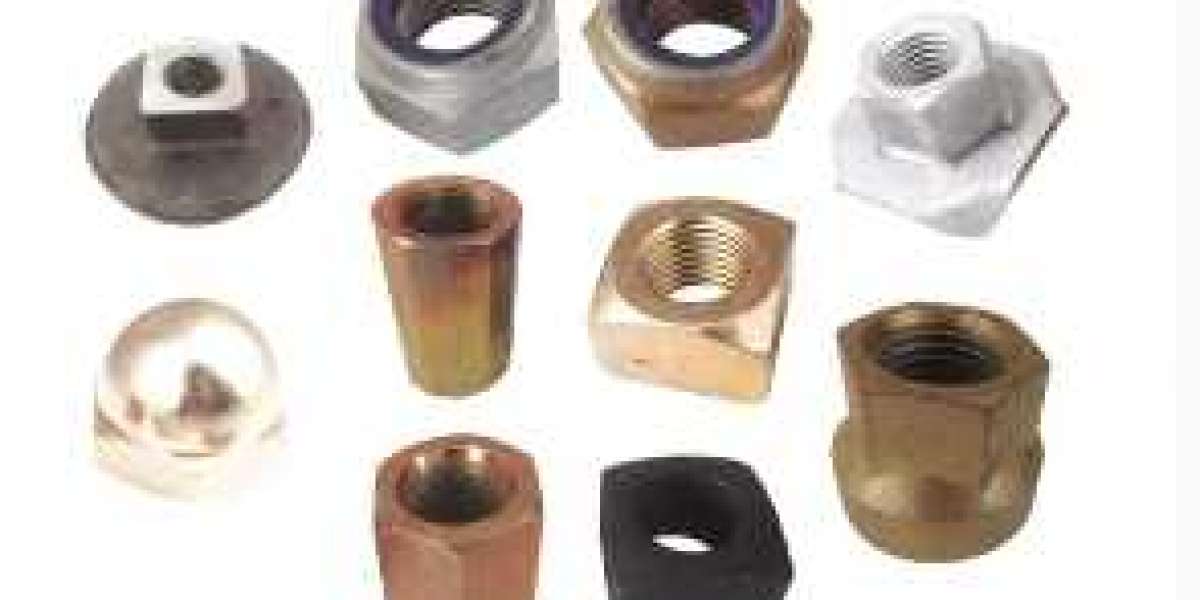
Rail nuts play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation and safety of railway systems. Nantong Longyu Track Materials Co., Ltd., a renowned manufacturer of railway fastening systems, takes great pride in producing top-quality rail nuts. In this article, we will delve into the importance of rail nuts, their wide range of applications, and the intricate manufacturing process involved.
Definition and Purpose of Rail Nuts
Rail nuts, also known as rail anchor nuts or rail clip nuts, are specialized fasteners used in railway systems to secure rails to the sleepers or ties. These nuts play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the track, ensuring the safe and smooth operation of trains.
Types of Rail Nuts
Rail nuts come in various types, each designed to meet specific requirements and conditions. The most common types include:
Square Rail Nuts: These nuts have a square shape and are widely used in railway systems worldwide. They provide a secure and reliable connection between the rail and the sleeper.
Hexagonal Rail Nuts: Hexagonal rail nuts, as the name suggests, have a hexagonal shape. They offer enhanced grip and are often used in high-speed rail systems where stability is of utmost importance.
Slotted Rail Nuts: Slotted rail nuts have slots on their sides, allowing for easy installation and adjustment. They are commonly used in situations where frequent maintenance and adjustments are required.
Material Selection for Rail Nuts
The choice of material for rail nuts is crucial to ensure their durability and performance. Rail nuts are typically made from high-quality steel, such as carbon steel or alloy steel. These materials provide excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance, ensuring the longevity of the rail nuts in demanding railway environments.
Applications of Rail Nuts
Rail nuts find extensive applications in railway systems worldwide. Some of the key applications include:
Track Construction: Rail nuts are used during the initial construction of railway tracks to secure the rails to the sleepers. They provide a strong connection that can withstand the forces exerted by passing trains.
Track Maintenance: Rail nuts are also used during track maintenance and repair activities. They allow for easy removal and replacement of damaged rails, ensuring the continuous operation of the railway system.
Track Upgrades: Rail nuts are essential when upgrading existing railway tracks. They enable the installation of new rails or the replacement of worn-out components, improving the overall performance and safety of the track.
Manufacturing Process of Rail Nuts
The manufacturing process of rail nuts involves several steps to ensure the production of high-quality and reliable fasteners. The process typically includes the following stages:
Material Selection: High-quality steel is carefully chosen for its strength and durability.
Forging: The selected steel is heated and shaped using forging techniques to form the desired rail nut shape.
Machining: The forged rail nuts are then machined to achieve precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
Heat Treatment: The rail nuts undergo a heat treatment process to enhance their mechanical properties, such as hardness and strength.
Surface Treatment: Surface treatments, such as galvanization or coating, are applied to protect the rail nuts from corrosion and improve their appearance.
Quality Control: The finished rail nuts undergo rigorous quality control inspections to ensure they meet the required standards and specifications.
Advancements in Rail Nut Technology
Over the years, advancements in rail nut technology have led to improved performance and safety in railway systems. Some notable advancements include:
Self-Locking Rail Nuts: Self-locking rail nuts incorporate innovative locking mechanisms that prevent loosening due to vibrations or other external factors. This technology enhances the stability and reliability of the rail connection.
Anti-Corrosion Coatings: The development of advanced anti-corrosion coatings has significantly extended the lifespan of rail nuts, reducing maintenance requirements and costs.
Lightweight Materials: The use of lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys, in rail nut manufacturing has resulted in reduced weight and improved fuel efficiency in railway systems.
Rail Nut Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and regular maintenance of rail nuts are essential to ensure their optimal performance and safety. The installation process involves securely fastening the rail nuts to the sleepers using appropriate tools and techniques. Regular inspections and maintenance activities, such as checking for loose nuts, corrosion, or wear, should be conducted to identify and address any issues promptly.
Importance of Rail Nut Safety
Rail nut safety is of utmost importance in railway systems to prevent accidents and ensure the smooth operation of trains. Loose or damaged rail nuts can lead to track misalignment, derailments, or other hazardous situations. Therefore, regular inspections, maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial to maintaining the integrity and safety of rail nut connections.
Conclusion
Rail nuts play a vital role in the efficient functioning and safety of railway systems. Their secure connection between the rails and sleepers ensures the stability and integrity of the track, allowing for the safe and smooth operation of trains. With advancements in technology and manufacturing processes, rail nuts continue to evolve, providing enhanced performance, durability, and safety. Proper installation, maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines are essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of rail nut connections in railway systems.